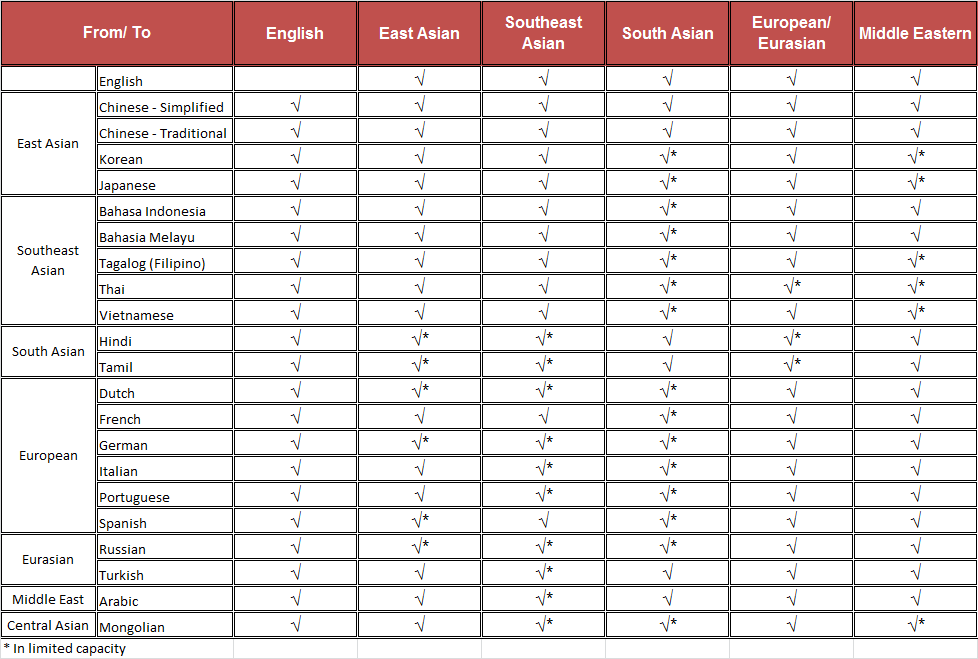
Language Pairs Translations

At Berlo, we provide translation for the following pairs of languages:
- East Asian Languages
- Southeast Asian Languages
- South Asian Languages
- European Languages
- Middle East Languages
EAST ASIAN LANGUAGES
In a more focused sense, East Asian languages refer to those languages that have been influenced by Classical Chinese (文言文) and the Chinese writing system (汉文), and mainly cover Chinese, Japanese, Korean and Vietnamese. However, since modern Vietnamese is no longer written with Chinese characters, only the first three are included in the grouping (CJK).
Simplified Chinese characters (简体字) are officially used in People’s Republic of China and in Singapore. In an attempt to increase literacy, the simplification movement was started by Mao Zedong in the 1950s in People’s Republic of China, greatly simplifying both structure of character forms and the total number of standardized characters. Traditional Chinese characters (繁體字) are currently used in Hong Kong, Republic of China (Taiwan) and Macau. Overseas Chinese generally use Traditional Chinese characters, but the Simplified Chinese version is generally used among mainland Chinese immigrants.
One key difference between East Asian languages and English lies in the sentence syntax, among others. Frequently, East Asian languages are constructed with topic-comment syntax, where the first segment is composed of the topic, and a comment comprises the second. On the other hand, English sentences are generally constructed with the comment coming before the topic. The following example illustrates this:
English: I have already bought tomorrow’s breakfast.
Chinese (Simplified): 明天的早餐我已经买了。(Tomorrow’s breakfast I have already bought.)
In both cases, the topic (tomorrow’s breakfast) and comment (I have already bought) are the same; however, the construction of one is the reverse of the other.
This is just a simple illustration, and the factor is one of those to be considered in translation, interpretation or transcription work. As the sentence gets more complicated and get embedded with more phrases and complex, technical terms, the fluency, experience and field understanding of the translator become more indispensable, and Berlo Translations is confident to claim that our translators have both the technical capability to work around complex statements and the background needed to understand the specialized terms of the content.
SOUTHEAST ASIAN LANGUAGES
From a geographical sense, Southeast Asian languages can be classified into Malayo-Polynesian, Sino-Tibetan and Mon-Khmer languages.
Malayo-Polynesian languages are estimated to have 300 to 500 tongues, and are understood by people in Madagascar, the Malay Peninsula, Indonesia and New Guinea, the Philippines, Melanesian, Micronesian and Polynesian Islands and New Zealand. Although not always as a first language, these languages have come to be widely used in these countries. Writing varies, as some forms are based on Roman alphabet (like Bahasa Malay, Indonesian and Tagalog), while the others are from Indian or Arabic scripts.
Sino-Tibetan languages can be classified into Tibeto-Burman or Sino-Siamese (Thai). The classification of a number of the languages suggested for the Sino-Tibetan family and its various subfamilies is still unresolved, and more work must be done before general agreement is reached.
Languages of the Mon-Khmer subfamily include Cambodian (or Khmer), Mon (or Talaing), and a number of other languages. Grammatically, the Mon-Khmer languages make great use of affixes (prefixes, infixes, and suffixes). Different linguistic elements, each of which exists separately and has a fixed meaning, are often joined to form one word.
SOUTH ASIAN LANGUAGES
South Asia is the home to hundreds of languages. Hindi is the most widespread language of India. The Indian census takes the widest possible definition of “Hindi” as a broad variety of “Hindi Languages”, and the native speakers of Hindi so defined account for about 40% of Indians.
EUROPEAN LANGUAGES
The Indo-European language family is composed of many subgroups, they are spoken throughout Europe and particularly dominate Western Europe. Among these subgroups are the Romance, Germanic and Slavic branches.
The Romance languages are spoken by about 600 million people across the globe. All of these languages derive from Latin, and the five national standard languages that are recognized include French, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese and Romanian. On the other hand, the Germanic languages are spoken on every continent by about 450 million people. Most people here speak English, but German, Dutch and even the Scandinavian languages remain spoken in former colonies all over the world.
The Slavic languages are spoken in Eastern Europe and Russia, this is the harder of the three language groups to learn. They are most closely related to the Baltic languages of Lithuania and Latvia. For someone interested in learning Slavic languages, Polish, Serbian, Croatian and Russian are the most useful. It will probably be easier to begin with the Western languages as they use the Roman alphabet. Russian will seem very easy if Croatian or Serbian has been learned first.
MIDDLE EAST LANGUAGES
The top three languages, in terms of numbers of speakers are Arabic, Persian and Turkish. Various other languages are also spoken in the Middle East.
Arabic is the most widely spoken language in the Middle East, being official in all the Arab countries. It is also spoken in some adjacent areas in neighboring Middle Eastern non-Arab countries.
The second-most widely spoken language is Persian. The language belongs to the Indo-Iranian branch of the family of Indo-European languages, and is much influenced by Arabic and Aramaic languages.
The third-most widely spoken language, Turkish, is confined to Turkey, which is also one of the region’s largest and most populous countries. It is also present in certain areas of neighboring countries as well. It is a member of the Turkic languages, which have their origins in Central Asia.

